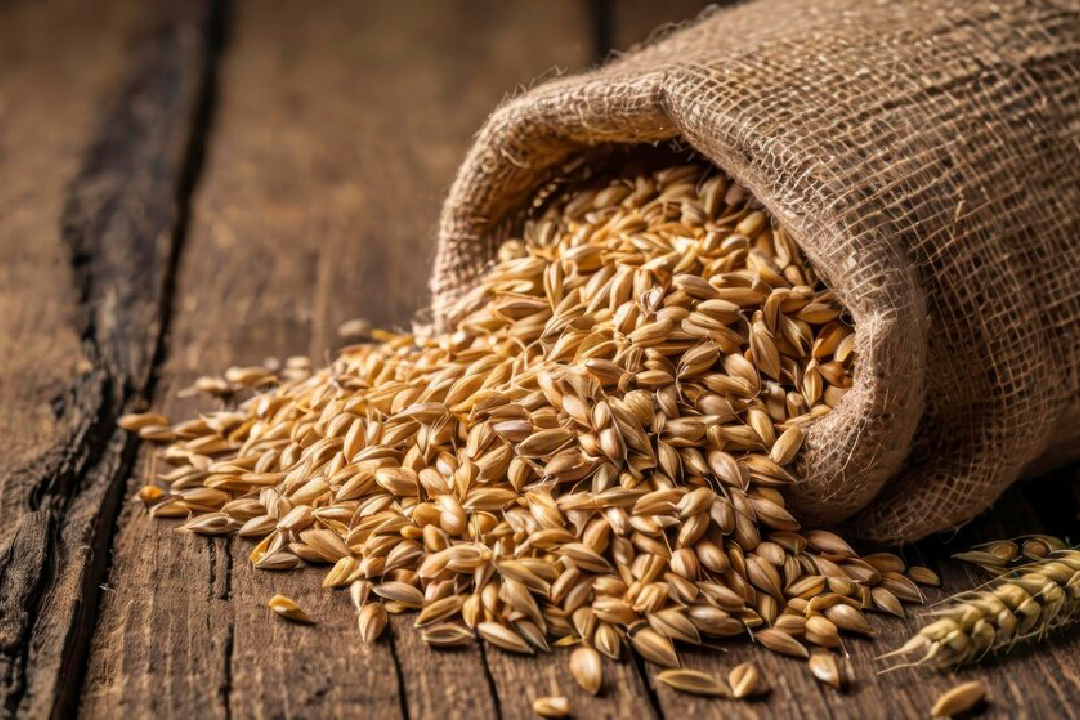
Barley is one of the first grains cultivated by humans. Evidence shows that barley has been cultivated since about 10,000 years ago, especially in Eurasia.
Globally, 70% of barley production is used as animal fodder. While 30% is used as a fermentable material for beer and some distilled drinks, as well as in various foods such as soups and stews and in barley bread. Barley seeds are usually used in the traditional way to prepare malt.
Barley, one of the basic and widely used products in the food industry, has long played an important role in human nutrition. This plant, which belongs to the cereal family, has been used by humans since ancient times to prepare various food products.
There are three varieties of barley: six-piled, two-piled and four-piled barley. This plant is more compatible than wheat.
It is rich in vitamins and a plant with relatively cooling properties, which is beneficial for the health of the intestines and digestive system.
Compatibility of the barley plant
This plant is one of the most compatible cereals.
- Favorable weather conditions
- Fertile soil with high water holding capacity
- Soils with pH between 7 and 8.
This plant is more resistant to drought than wheat, and therefore, in climates where water limits grain production, barley can produce the most crops.
Barley needs less moisture than wheat to germinate. In cases where the plant dries up due to the lack of moisture after the seed has germinated, the plant will start growing again with a favorable moisture condition.
types of barley
This grain has different types in different classifications.
- The most common method of classifying barley is in rows (two, four or six rows of seeds per head).
- Another classification is wild and cultivated barley. Two-row wild barley and six-row cultivated barley
Regarding the reaction to temperature, there are three types of atmosphere:
- Spring type that is sensitive to cold and therefore planted in spring.
- Autumn type: it is planted in autumn and does not produce clusters until spring.
- Its middle type is less resistant to cold. It is cultivated in relatively tropical areas. Both in spring and fall
harvest time
To determine the right date for harvesting, you should pay attention to the following indicators:
- Seed moisture
- Standards of a specific atmosphere (color, size)
- grain hardness
- Straw color
- Knot color and strength
How to consume barley
- Oatmeal: can be easily boiled in water or milk. For example, breakfast or snack.
- Barley: Barley can be used as a staple food. Example: in soup or stew
- Oatmeal: Oatmeal can be used as a cereal. For example: in salad or salad.
Properties
- Lower cholesterol levels
- It helps to lose weight
- It reduces the risk of cancer
- Reduction of arthritis symptoms
- It helps to maintain the health of teeth and bones
- Fight against diabetes
- Prevents gallstones
- It is useful for pregnant women
- It improves digestion and constipation
- Strengthen the immune system
- It reduces the risk of asthma in children
- Brightens the skin
- Prevents urinary tract infections
- It protects against arteriosclerosis
- It helps to treat anemia
- Improve gut health
- Prevention of kidney stones
- The body’s resistance to flu and colds
- Increasing the body’s metabolic rate
- Helping to grow and repair body tissues
- Has anti-aging properties
- Help hair grow
Complications of high consumption
- Allergies: Some people may be allergic to barley. Allergy symptoms can include itching, swelling, rashes, breathing problems, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
- Gastrointestinal problems: Due to the high fiber content, high consumption of oats may cause digestive problems such as bloating, gas, heartache and diarrhea in some people.
- Gluten: Oats contain gluten and for people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, consumption of oats can cause serious problems.
- Drug interactions: Barley may interact with some medications. For example, the fiber in oats can reduce the absorption of some medications.
- Excessive consumption: excessive consumption of barley and its products can lead to problems such as imbalance of nutrients in the body. For example, consuming too much fiber without drinking enough water can lead to constipation. It is important to balance barley intake and combine it with other foods.
Nutritional value table
| The main constituent | Amount per 100 grams |
| energy (calories) | 354 kcal |
| Carbohydrate | 73.48 grams |
| Protein | 12.48 grams |
| fat | 2.30 grams |
| water | 9.44 grams |
| fiber | 17.30 grams |
| sugar | 0.80 grams |
| Cholesterol | 0.00 mg |
| vitamins | |
| The name of the vitamin | Amount per 100 grams |
| Vitamin A | 1.00 micrograms |
| Vitamin D | 0.00 µg |
| Vitamin E | 0.57 mg |
| Vitamin K | 2.20 micrograms |
| Vitamin C | 0.00 mg |
| Thiamine (B1) | 0.65 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) | 0.29 mg |
| Niacin (B3) | 4.60 mg |
| Choline (B4) | 0.00 mg |
| pantothenic acid (B5) | 0.28 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.32 mg |
| Folate (B9) | 19.00 micrograms |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.00 mg |
| minerals | |
| The name of the mineral | Amount per 100 grams |
| calcium | 33.00 mg |
| iron | 3.60 mg |
| magnesium | 133.00 mg |
| phosphorus | 264.00 mg |
| Potassium | 452.00 mg |
| sodium | 12.00 mg |
| Roy | 2.77 mg |
| copper | 0.50 mg |
| Manganese | 1.94 mg |
| selenium | 37.70 micrograms |






















“This is exactly what I was looking for, thank you!”
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Many thanks for providing these details.
very informative articles or reviews at this time.
very informative articles or reviews at this time.